Nearly one in five teachers believe the attainment gap will “increase substantially” after this year’s summer exams, the first since the pandemic began.
The Sutton Trust has published research into the impact of Covid on this year’s exams and university admissions cycle, ahead of results days later this month.
The charity called on universities to give additional consideration to students from disadvantaged backgrounds, amid warnings that more students will be left without a place this summer.
The trust also called for Ofqual to consider adaptions to next year’s exams.
Pupils sat the first set of GCSE and A-level exams since 2019 this year, and although there were some adaptations like advance notice of topics, this year’s students will be graded more harshly than those given teacher-assessed grades in 2021.
The charity’s chief executive James Turner said the research “highlights that the impacts of the pandemic on education are far from over – and the consequences are still being felt among young people and their teachers”.
Savanta surveyed 434 university applicants while TeacherTapp polled 4,089 teachers in England.
Here’s what you need to know…
1. Most teachers fear the gap will widen
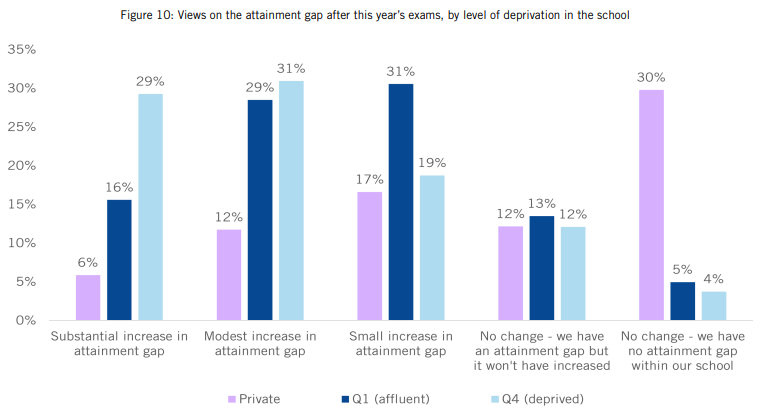
Seventy-two per cent of teachers thought the attainment gap at their school will widen with the return of national exams, with 19 per cent believing it will “increase substantially”.
Those working in deprived schools were 13 percentage points more likely to think the increase would be substantial, at 29 per cent, compared to 16 per cent of those working in more affluent schools.
In 2021, longstanding attainment gaps for both black and poorer students widened. But Ofqual was unable to untangle whether this was down to Covid lost learning or the use of teacher grades last year.
2. A third feel 2022 grade boundaries ‘too strict’
This year, grade boundaries will sit midway between 2021 and 2019, the last time exams were sat before the pandemic.
While 57 per cent of teachers thought this approach was about right, 29 per cent thought it was too strict.
Thirty-five per cent of teachers in the most deprived schools thought it was too strict, compared to 27 per cent in more affluent schools.
3. Nearly half don’t think mitigations go far enough
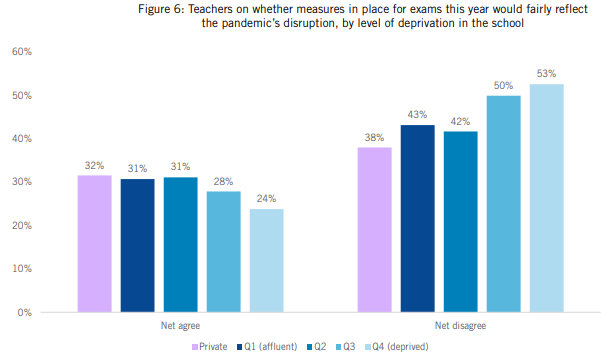
While 29 per cent of teachers believe that this year’s mitigations, such as advance information and topic optionality, will fairly reflect pandemic disruption, 45 per cent disagreed.
Those working in state schools were more likely to disagree at 46 per cent, compared to 38 per cent at private schools.
Over half of teachers in the most deprived schools disagreed, compared to 43 per cent of those in schools with more affluent intakes.
4. Poorer schools covered less content and fewer mocks
The majority (80 per cent) of A-level teachers said they were able to cover over 90 per cent of the content included in advance information.
But those working at the most deprived schools were 22 percentage points less likely to report this than those at affluent schools (67 per cent vs 88 per cent).
Most students sitting GCSEs and A-levels this year won’t have sat formal exams before.
The Sutton Trust looked at how many students had to sit mock exams under exam conditions.
It appears students in the most deprived schools were less likely to have experienced exams, with 68 per cent of teachers saying they had done so in an exam hall under exam conditions. This compares to 87 per cent of teachers in more affluent schools.
5. 1 in 5 students missed a month of school
Over a third (34 per cent) of students taking exams said they missed 11 days or more this academic year.
But 21 per cent said they had missed more than 20 days – equivalent to four or more weeks of class time.
It echoes analysis by FFT Education Datalab earlier this year, which found year 11 pupils missed more than one in ten lessons in March in every region except London.
6. Ethnic minority students believe they are further behind
Two thirds of students believed they had fallen behind with their studies compared to pre-pandemic. State school students were more likely to report this (64 per cent) compared to 51 per cent of private school students.
A third believed they had fallen behind their peer group as a result of the pandemic. Ethnic minority students were much more likely to think they lagged behind peers (41 per cent) compared to white university applicants (23 per cent).
Private school students were more likely to think they had fallen behind peers (38 per cent) compared to 28 per cent of state school students.
And those from working class backgrounds were eight percentage points more likely to be concerned about their grade this summer, at 70 per cent, compared to 62 per cent from middle class backgrounds.
















Your thoughts