A growing number of young people report keeping their suffering to themselves. Simon Walker explains the evidence and how to support them
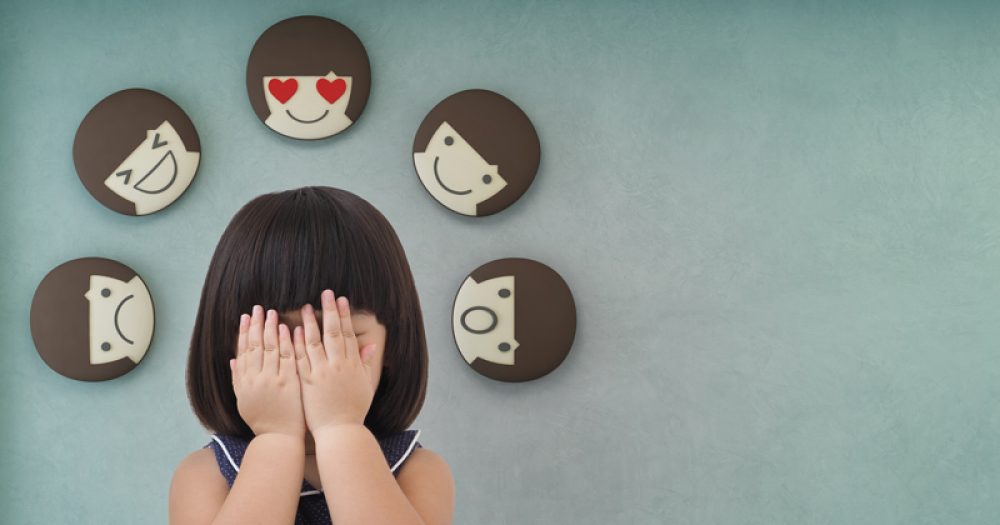
It used to be that most pupils with challenging emotional and behavioural difficulties (EBD) were difficult to miss. Challenging needs almost always meant challenging behaviours. But not anymore. The majority of pupils facing challenging needs today are currently hiding them from teachers and peers alike, and you may well be missing them.
Since 2015 my organisation, STEER Education, has been tracking pupils’ social-emotional development as they progress from years 3 to 13. With six years of data from over 70,000 pupils, we are the only UK organisation to have large-scale pre-, during and post-pandemic data.
One of the measures we track is self-disclosure. Think of each pupil having a front and a backstage; low-disclosing pupils hold what they are really thinking and feeling backstage – which you cannot see. What you see is their frontstage, which is a deflection.
Since 2016, there has been a steady increase in pupils becoming low-disclosing. One possible driver of this is the rise in social media use, an environment which punishes young people for disclosing anything which may be mocked. But the pandemic has accelerated these hidden risks.
Low-disclosing boys have also increased by 20 per cent
Before Covid, for example, among girls in secondary schools, nearly 6 in 10 masked their thoughts, feelings, needs and ideas from those at school – friends and teachers alike. That number has now risen to 8 in 10, and low-disclosing boys have also increased by over 20 per cent.
What we are seeing is a generation of young people turning inwards. The pandemic has made them more self-contained and autonomous, and curtailed their relationships and social interactions. At the same time, parents and teachers have been much less available to them.
The mental health implications of this low self-disclosure are serious. Think of the year 11 boy completing your ‘wellbeing recovery survey’; he won’t tell you he is struggling with exam pressures or bullying. Or think of the year 9 girl meeting her tutor; she’ll try to avoid any indication she is struggling with anxiety or that her situation at home is difficult.
More concerningly, 40 per cent of such girls are now developing a psychological pattern called internalised control. A mechanism for coping when the world seems both unsafe and unavailable, it involves containing our thoughts and feelings internally, often by ruminating and worrying. It tends to lead to high cortisol levels. It sometimes escalates into unhealthy self-soothing activities.
Worse still, these hidden needs risk becoming entrenched into long-term problems if we don’t deal with them. But how do you help someone you don’t know needs it? Our four-step guidance plan, under the acronym VEIL, can help.
- Validate losses and focus resources
Pupils may be anxious about what they have lost through the pandemic. Validate those feelings but explain how you will be putting support in place. Don’t simply focus on exam years. Year 6 pupils are especially anxious about transition to secondary school, and Year 10 at teaching loss.
- Equip your team and anticipate concerns
Don’t mistake quietness for wellness. Remind pupils they can contact tutors or trusted staff through email, which may feel less threatening. Train tutors to notice when their tutees’ mood, routine, or attitude changes and ask “How are you finding things at the moment?”
- Invite year 11 and year 13 to contribute post-exams
Consider how you can extend the school provision for years 11 and Y13 after their exams rather than letting them drift through more damaging unaccompanied summer months. Why not invite them to train as your peer resource for the next step.
- Build peer listening into your school structure
Consider how to build in peer listening into the school from September. Peer listeners may be more effective channels for pupils to share their concerns than adults.
The major problems our pupils are grappling with are behind this veil. Unless we create ways to lift it and face up to them, the pandemic’s impact risks haunting them – and us – for years to come.















Your thoughts